Changing careers is an expensive term. Its weight is as much
as the first salary on a new job. Why wouldn't choose
something that we understand plus something that is an
uprising on a job market?
Management might be an area where some of us have worked
before or even had experiences like this ourselves - in which
case knowing how things work should help out. But what about
Software Product Manager? What are we know about this
discipline? As we narrow down the job descriptions, it becomes
clear that this type of profession needs specialization.
Software Product Manager is a specialized profession that
requires special mindset to be successful. This text is made
for a better understanding of effective techniques which
produce better software products. As we comprehend the
position and the role of SMP, it will be easier to adopt a way
of disciplining ourselves. Better discipline-closer to
beginning the new product. So, whether you are changing your
career or finding a meaning of a specific job position,
inspection in Software Product Management will not harm you.
Software Product Management, understanding
The Discipline.
Software product management is the discipline of building,
implementing, and managing a software product. It is a
discipline and process which governs a product from the
inspection to the market or customer delivery.
A software product manager needs an intuitive mind to assess
whether the project is meeting client expectations, as to be
able to work with a development team to solve clients'
problems.
Before diving into the job description keep in mind that
Project and Product management are two disciplines that
overlap. It is all about timing, and that fact uses both
Project and Product management. At some point, it is requested
from the Product Manager to act as Project Manager meaning
uses some of Project manager duties or/and responsibilities.
And vice versa.
To unwrap SPM discipline, we need to understand what a
Software Product Manager’s point of view is. The number of
goals or viewpoints are needed to understand to achieve better
software.
The first aim will be providing the right software products
for the clients. It has to meet their needs, solve their
problems, and end up happy with it. To be a successful
product, the software needs validation. That would be the
medal for this phase.
The second aim has a focus on meeting the needs of customers
by having software that's been designed and implemented
properly. This viewpoint aims to have the software product
done right. Reviews and tests are run by developers, to make
sure they're following what was required for each stage in
order not only to uphold quality standards but also improve
upon them where possible. When the process in this phase is
done, verification is awaiting.
The third perspective is to have the software project managed
right. This means adopting just enough processes and suitable
practices so that everyone involved in organizing work with a
high understanding of what is their role. Responsibilities are
clear and this approach eases communications and feedback.
Role of
Software Product Manager.
To achieve better software, three goals need to be met: the
right product (which is defined as something that solves a
customer’s problem), done right, and managed correctly. The
SPM has been tasked with ensuring this success for any
company's products through their management skillset.
The product manager is not just a project leader, but also
someone who can speak to clients and developers on their
terms. The key responsibilities of the role include
understanding what makes up your end-users' experience as well
as effectively communicating with those on development teams
for motivation. One must be able to communicate clearly so
that both parties understand one another needs.
The challenge for product managers is that they do not have a
clearly defined role. The design and engineering professions
have been able to segment themselves by specializing in one
specific area but this talent does not exist within the realm
of consumer products. As the picture says more than 1000
words, here is an example:
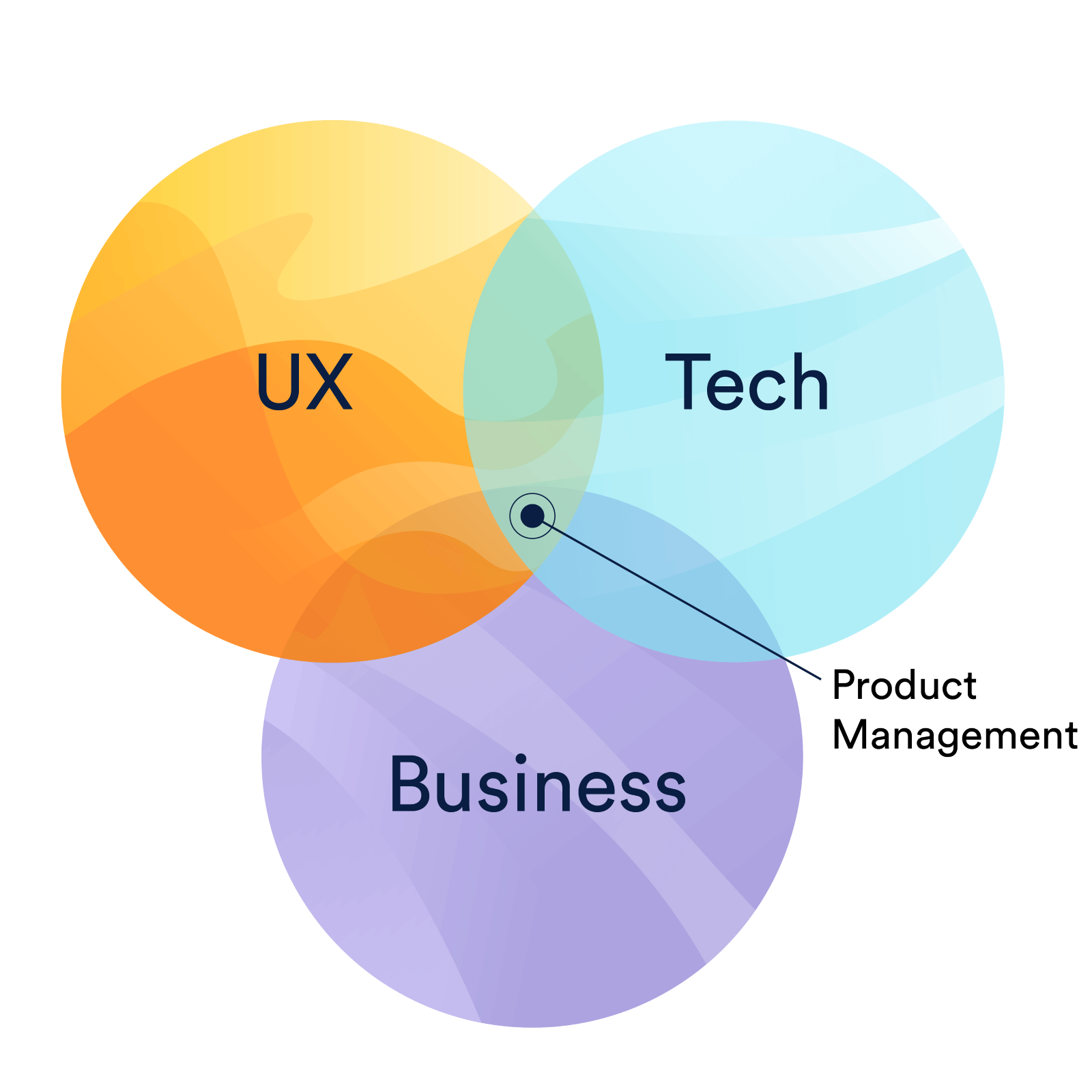 Venn diagram helps us see what is SPM consists of. That is
the intersection of user experience, business, and
technology.
Venn diagram helps us see what is SPM consists of. That is
the intersection of user experience, business, and
technology.
The Product Manager is the person who makes sure projects
don't fail!
The summary we've come to know and love about this position is
that SPM is in charge of project success. The Product Manager
is a critical component of any project team. They are
responsible for managing the entire life cycle from
requirements gathering, analysis and design through testing to
launching new products or service offerings on time with
minimal budget overruns so that their clients can focus on
core business activities rather than logistics.
How to discipline ourselves for the
SPM position?
For the task to be completed successfully and efficiently by
the Product Manager, a diverse set of skills are required.
From both design thinking as well as a marketing strategy -
two fields that have been oftentimes studied by different
disciplines but come together here at one point: product
management.
What can be said about skills that a Product Manager requires?
Refer to this above, here what is winning combination:
-
Communication skills: The
importance of well-presented information cannot be
overstated. Poorly presented data can cause missed deadlines
and unhappy employees, which means that the business suffers
as a result.
-
Diplomacy: Listening and
empathizing are the key. It's important to find common
ground with both sides before moving forward, so try
settling an argument by asking "What do we agree on?"
-
Technical knowledge: Small
steps on a big technology trip will improve your technical
proficiency. Needleless is to be a coding magician, but
there is a certain area of skills that is in front of you to
discover.
-
Persuasion skills:
Persuasive people are skilled at changing or influencing the
behaviors, beliefs, and attitudes of others. That includes
using all sorts of different techniques like humor or
compelling arguments based on your personal experiences as
well as some statistics.
-
Delegation skills: To ensure
your product is marketable, relying on smart people within
the organization is the right way of doing it. If they are
willing and able to handle, then give them some of these
responsibilities so that everyone can succeed together.
-
Strategic thinking: It is
the key to success for any company and a highly desirable
Manager skill. It ensures that focuses stay on critical
factors and variables that will influence the long-term
success of a business, or/and team.
-
Self-management:
Self-management means understanding personal responsibility
in different aspects of life, and doing what's necessary to
fulfill that duty.
-
Interpersonal skills:
Product management isn’t all about being a taskmaster—it’s
about supporting and empowering others by understanding
their strengths and weaknesses. Having enough influence to
keep everyone working together toward the same goal is a
professional SPM goal.
-
Research/analytical skills:
Skills that combine data mining, metrics interpreting, and
reporting are something that will help grow successful SPM.
-
Understand the user lifecycle:
Covering all the aspects of the product development life
cycle is the Product Manager’s job. Growing product from
“its birth” contributes a deeper understanding of something
that this role is in charge of.
If it adds a passion for solving the problem to this mix of
skills, it wouldn’t be a problem to manage software products.
How success is measured?
When the answer is wanted, fully packed Software Project
Manager stands above his product asking himself the next
questions:
- Was it on-time delivery?
- Is it completed within budget?
- Is it delivered with all features complete?
But the measurements can also be taken from:
- The number of post-release bugs
- The support needed after a release
- The software product’s customer rating
- The revenue generated
-
And something that needs to be followed during the whole
process is the client’s satisfaction
As seen “measurements” are blend from standpoints, both
Product and Project management.
Conclusion
A successful Software Product Manager must have insight into
winning strategies. They are needed to make sure that they
can produce high-quality results meeting all necessary
specifications before time runs out on deadlines or budgets.
The product manager is the person who leads and manages one
or more products from their inception to phase-out. The
software's job includes creating customer value while
delivering measurable business benefits, collaborating with
cross-functional teams such as marketing, sales engineering,
etc. All that in order to achieve the goal by building a
quality product which all members are happy working on
together towards an ultimate success of the production.
If there is any profession that sits on an intersection on
multiple functions-that is Product Manager.
So, do you have the discipline to take over a new product?
